地址:北京市海淀区上地十街1号
电话:15132636097
河北介质损耗因数测试仪 安全措施
(1)高压保护:试品短路、击穿或高压电流波动,能迅速切断高压输出。
(2)CVT保护:设定自激电压的过流点,一旦超出设置的电流值,仪器自动退出测量,不会损坏设备。
(3)接地检测:仪器有接地检测功能,未接地时不能升压测量。
(4)防误操作:具备防误操作设计,能判别常见接线错误,安全报警。
(5)防“容升”:测量大容量试品时会出现电压抬高的“容升”效应,仪器能自动跟踪输出电压,保持试验电压恒定。
河北介质损耗因数测试仪 离子晶体的损耗
离子晶体的介质损耗与其结构的紧密程度有关。
紧密结构的晶体离子都排列很有规则,键强度比较大,如α-Al2O3、镁橄榄石晶体等,在外电场作用下很难发生离子松弛极化,只有电子式和离子式的位移极化,所以无极化损耗,仅有的一点损耗是由漏导引起的(包括本质电导和少量杂质引起的杂质电导)。这类晶体的介质损耗功率与频率无关,损耗角正切随频率的升高而降低。因此,以这类晶体为主晶相的陶瓷往往用在高频场合。如刚玉瓷、滑石瓷、金红石瓷、镁橄榄石瓷等
结构松散的离子晶体,如莫来石(3Al2O3·2SiO2)、董青石(2MgO·2Al2O3·5SiO2)等,其内部有较大的空隙或晶格畸变,含有缺陷和较多的杂质,离子的活动范围扩大。在外电场作用下,晶体中的弱联系离子有可能贯穿电极运动,产生电导打耗。弱联系离子也可能在一定范围内来回运动,形成热离子松弛,出现极化损耗。所以这类晶体的介质损耗较大,由这类品体作主晶相的陶瓷材料不适用于高频,只能应用于低频场合。Loss of ionic crystalsThe dielectric loss of ionic crystals is related to the tightness of their structure.The tightly structured crystal ions are arranged in a very regular manner, and the bond strength is relatively high, such as α- Al2O3, magnesium olivine crystals, etc., are difficult to undergo ion relaxation polarization under the action of an external electric field, only electronic and ionic displacement polarization, so there is no polarization loss. The only loss is caused by leakage conductivity (including intrinsic conductivity and impurity conductivity caused by a small amount of impurities). The dielectric loss power of this type of crystal is independent of frequency, and the tangent of the loss angle decreases with increasing frequency. Therefore, ceramics with such crystals as the main crystal phase are often used in high-frequency applications. Such as corundum porcelain, talc porcelain, rutile porcelain, magnesium olivine porcelain, etcIonic crystals with loose structures, such as mullite (3Al2O3 · 2SiO2) and muscovite (2MgO · 2Al2O3 · 5SiO2), have large voids or lattice distortions inside, containing defects and numerous impurities, and expanding the range of ion activity. Under the action of an external electric field, weakly connected ions in the crystal may penetrate the electrode and cause conductivity depletion. Weakly connected ions may also move back and forth within a certain range, forming thermal ion relaxation and resulting in polarization loss. So the dielectric loss of these crystals is relatively high, and ceramic materials with these types of crystals as the main crystal phase are not suitable for high frequencies and can only be applied in low frequency situations.
高分子材料的损耗
高分子聚合物电介质按单体单元偶极矩的大小可分为极性和非极性两类。一般地,偶极矩在0~0.5D(德拜)范围内的是非极性高聚物;偶极矩在0.5D以上的是极性高聚物。非极性高聚物具有较低的介电常数和介质损耗,其介电常数约为2,介质损耗小于10-4;极性高聚物则具有较高的介电常数和介质损耗,并且极性愈大,这两个值愈高。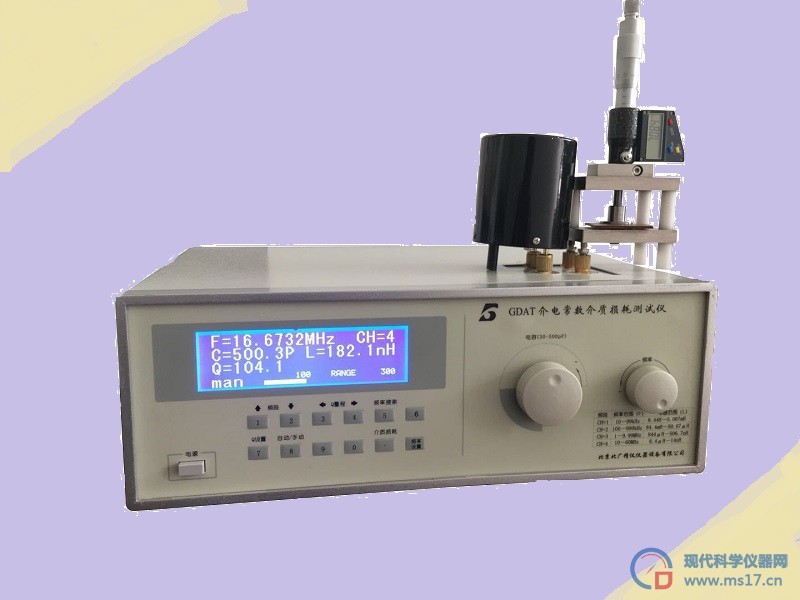
高聚物的交联通常能阻碍极性基团的取向,因此热固性高聚物的介电常数和介质损耗均随交联度的提高而下降。酚醛树脂就是典型的例子,虽然这种高聚物的极性很强,但只要固化比较完全,它的介质损耗就不高。相反,支化使分子链间作用力减弱,分子链活动能力增强,介电常数和介质损耗均增大。
高聚物的凝聚态结构及力学状态对介电性景响也很大。结品能抑制链段上偶极矩的取向极化,因此高聚物的介质损耗随结晶度升高而下降。当高聚物结晶度大于70%时,链段上的偶极的极化有时完全被抑制,介电性能可降至最低值,同样的道理,非晶态高聚物在玻璃态下比在高弹态下具有更低的介质损耗。此外,高聚物中的增塑利、杂质等对介电性能也有很大景响。Loss of polymer materialsPolymer dielectrics can be divided into two categories based on the dipole moment of monomer units: polar and non-polar. Generally, non-polar polymers have a dipole moment in the range of 0~0.5D (Debye); Polymers with a dipole moment above 0.5D are polar polymers. Non polar polymers have lower dielectric constant and dielectric loss, with a dielectric constant of about 2 and a dielectric loss of less than 10-4; Polar polymers have higher dielectric constant and dielectric loss, and the greater the polarity, the higher these two values.The crosslinking of polymers can usually hinder the orientation of polar groups, so the dielectric constant and dielectric loss of thermosetting polymers decrease with the increase of crosslinking degree. Phenolic resin is a typical example. Although this polymer has strong polarity, as long as it is cured completely, its dielectric loss is not high. On the contrary, branching weakens the intermolecular forces, enhances the activity of molecular chains, and increases the dielectric constant and dielectric loss.The condensed structure and mechanical state of polymers also have a significant impact on their dielectric properties. The product can suppress the orientation polarization of the dipole moment on the chain segment, so the dielectric loss of the polymer decreases with increasing crystallinity. When the crystallinity of the polymer exceeds 70%, the polarization of the dipole on the chain segment is sometimes completely suppressed, and the dielectric performance can be reduced to the lowest value. Similarly, amorphous polymers have lower dielectric loss in the glass state than in the high elastic state. In addition, the plasticizers and impurities in polymers also have a significant impact on the dielectric properties.
介质损耗:绝缘材料在电场作用下,由于介质电导和介质极化的滞后效应,在其内部引起的能量损耗。也叫介质损失,简称介损。在交变电场作用下,电介质内流过的电流相量和电压相量之间的夹角(功率因数角Φ)的余角δ称为介质损耗角。
损耗因子也指耗损正切,是交流电被转化为热能的介电损耗(耗散的能量)的量度,一般情况下都期望耗损因子低些好。
标准配置:
高配Q表 一只
试验电极 一只 (c类)
电感 一套(9只)
电源线 一条
说明书 一份
合格证 一份
保修卡 一份
测试注意事项
a.本仪器应水平安放;
b.如果你需要较精确地测量,请接通电源后,预热30分钟;
c.调节主调电容或主调电容数码开关时,当接近谐振点时请缓调;
d.被测件和测试电路接线柱间的接线应尽量短,足够粗,并应接触良好、可靠,以减少因接线的电阻和分布参数所带来的测量误差;
e.被测件不要直接搁在面板顶部,离顶部一公分以上,必要时可用低损耗的绝缘材料如聚苯乙烯等做成的衬垫物衬垫;
f.手不得靠近试件,以免人体感应影响造成测量误差,有屏蔽的试件,屏蔽罩应连接在低电位端的接线柱。
Testing precautionsa. This instrument should be placed horizontally;b. If you need to measure more accurately, please turn on the power and preheat for 30 minutes;c. When adjusting the main capacitor or digital switch of the main capacitor, please adjust slowly when approaching the resonance point;d. The wiring between the tested component and the test circuit terminals should be as short as possible, thick enough, and have good and reliable contact to reduce measurement errors caused by the resistance and distribution parameters of the wiring;e. The test piece should not be placed directly on the top of the panel, at least one centimeter away from the top. If necessary, a low loss insulation material such as polystyrene can be used as a lining material for cushioning;f. Hands should not approach the test piece to avoid measurement errors caused by human induction. For shielded test pieces, the shielding cover should be connected to the low potential terminal terminal.
温度
损耗指数在一个频率下可以出现一个最大值,这个频率值与电介质材料的温度有关。介质损耗因数和电容率的温度系数可以是正的或负的,这取决于在测量温度下的介质损耗指数最大值位置。
为什么介电常数越大,绝缘能力越强?
因为物质的介电常数和频率相关,通常称为介电系数。
介电常数又叫介质常数,介电系数或电容率,它是表示绝缘能力特性的一个系数。所以理论上来说,介电常数越大,绝缘性能就越好。
电离损耗
电离损耗(又称游离损耗)是由气体引起的,含有气孔的固体介质在外加电场强度超过气孔气体电离所需要的电场强度时,由于气体的电离吸收能量而造成指耗,这种损耗称为电离损耗。
信号源频率覆盖范围
频率范围CH1:0.1~0.999999MHz, CH2: 1~9.99999MHz,
CH3:10~99.9999MHz, CH1 :100~160MHz,
试样的几何形状:
测定材料的电容率和介质损耗因数,最好采用板状试样,也可采用管状试样。
在测定电容率需要较高精度时,最大的误差来自试样尺寸的误差,尤其是试样厚度的误差,因此厚度应足够大,以满足测量所需要的精确度。厚度的选取决定于试样的制备方法和各点间厚度的变化。对 1%的精确度来讲,1.5 mm的厚度就足够了,但是对于更高精确度,最好是采用较厚的试样,例如6 mm-12 mm 。测测量厚度必须使测量点有规则地分布在整个试样表面上,且厚度均匀度在士1%内。如果材料的密度是已知的,则可用称量法测定厚度 选取试样的面积时应能提供满足精度要求的试样电容。测量 10 pF的电容时,使用有良好屏蔽保护的仪器。由于现有仪器的极限分辨能力约 1 pF,因此试样应薄些,直径为 10 cm或更大些。
需要测低损耗因数值时,很重要的一点是导线串联电阻引人的损耗要尽可能地小,即被测电容和该电阻的乘积要尽可能小 同样,被测电容对总电容的比值要尽可能地大 第一点表示导线电阻要尽可能低及试样电容要小。第二点表示接有试样桥臂的总电容要尽可能小,且试样电容要大。因此试样电容最好取值为20 pF,在测量回路中,与试样并联的电容不应大于约5 pF。
陶瓷材料的损耗
陶瓷材料的介质损耗主要来源于电导损耗、松弛质点的极化损耗和结构损耗。此外,表面气孔吸附水分、油污及灰尘等造成的表面电导也会引起较大的损耗。
在结构紧密的陶瓷中,介质损耗主要来源于玻璃相。为了改善某些陶瓷的工艺性能,往往在配方中引人此易熔物质(如黏土),形成玻璃相,这样就使损耗增大。如滑石瓷、尖晶石瓷随黏土含量增大,介质损耗也增大。因面一般高频瓷,如氧化铝瓷、金红石等很少含有玻璃相。大多数电陶瓷的离子松弛极化损耗较大,主要的原因是:主晶相结构松散,生成了缺固济体、多品型转变等。 Loss of ceramic materialsThe dielectric loss of ceramic materials mainly comes from conductivity loss, polarization loss of relaxed particles, and structural loss. In addition, the surface conductivity caused by the adsorption of moisture, oil stains, and dust by surface pores can also cause significant losses.In tightly structured ceramics, the dielectric loss mainly comes from the glass phase. In order to improve the process performance of certain ceramics, it is often necessary to incorporate this fusible substance (such as clay) into the formula to form a glass phase, which increases the loss. As the clay content increases, the dielectric loss of talc ceramics and spinel ceramics also increases. Due to the fact that high-frequency ceramics such as alumina ceramics and rutile rarely contain glass phase. The ion relaxation polarization loss of most electric ceramics is relatively large, mainly due to the loose structure of the main crystal phase, the formation of solid deficient bodies, and the transformation of multiple types.
电容测量:1~205
主电容调节范围:18~220pF
准确度:150pF以下±1.5pF; 150pF以上±1%
注:大于直接测量范围的电容测量见后页使用说明
结构损耗
在高频电场和低温下,有一类与介质内邻结构的紧密度密切相关的介质损耗称为结构损耗。这类损耗与温度关系不大,耗功随频率升高而增大。
试验表明结构紧密的晶体成玻璃体的结构损耗都很小,但是当某此原因(如杂质的掺入、试样经淬火急冷的热处理等)使它的内部结构松散后。其结构耗就会大大升高。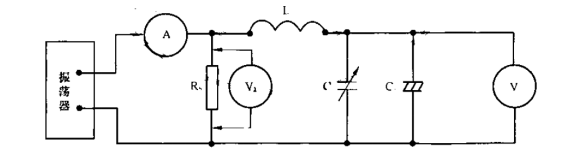
指另装置的技术特性:
工作电压±12V
在50Hz时电压灵敏度不低于1X10-6V/格, 电流灵敏度不低于2X10-9A/格
二次谐波 减不小于25db
三次谐波 减不小于50db
电桥测量灵敏度
电桥在使用过程中,灵敏度直接影响电桥平衡的分辨程度,为保证测量准确度,希望电桥灵敏度达到一定的水平。通常情况下电桥灵敏度与测量电压,标准电容量成正比。
在下面的计算公式中,用户可根据实际使用情况估算出电桥灵敏度水平,在这个水平上的电容与介质损耗因数的微小变化都能够反应出来。
DC/C或Dtgd=Ig/UwCn(1+Rg/R4+Cn/Cx)
式中:U为测量电压 伏特(V)
ω为角频率 2pf=314(50Hz)
Cn标准电容器容量 皮法(pF)
Ig通用指另仪的电流5X10-10 安培(A)
Rg平衡指另仪内阻约1500 欧姆(W)
R4桥臂R4电阻值3183 欧姆(W)
Cx被测试品电容值 皮法(pF)
设备保修两年,终身售后服务,两年内非人为损坏的零部件免费更换,保修期内接到用户邀请后, 最迟响应时间为2小时内,在与用户确认故障后,我公司会在48小时内派工程师到达现场进行免费服务,尽快查清故障所在位置和故障原因,并向用户及时报告故障的原因和排除办法 。